AT THE beginning of September, before political focus temporarily dimmed, the Welsh and UK Governments invited applications for Wales’s first freeport, which is planned to be up and running next year.
After years of wrangling, Welsh Ministers agreed to support freeport policies in Wales after the UK Government agreed delivering them would meet the Welsh Government’s demands for a “partnership of equals”.
Part of the agreement reached placed Wales on the same footing for starter funding after three years in which the UK Government refused to fund Wales to the same level as Scotland and England.
A Welsh freeport will be a special zone with the benefits of simplified customs procedures, relief on customs duties, tax benefits, and development flexibility.
Milford Haven Port Authority, which has already expressed interest in Freeport-status, to push the Haven’s claims to be the location of a Freeport in Wales.
WHAT IS A FREEPORT?
Freeports are a special area where normal tax and customs rules do not apply. These can be airports as well as maritime ports. At a Freeport, imports can enter with simplified customs documentation without paying tariffs.
Businesses operating inside designated areas in and around the port can manufacture goods using the imports and add value before exporting again without ever facing full tariffs or export procedures.
Suppose the goods move out of the Freeport into another part of the country. In that case, however, they must go through the full import process, including paying any tariffs.
The UK was previously home to several Freeports, including Liverpool, Southampton, and the Port of Tilbury.
The legislation governing them was not renewed in 2012 because – while the UK remained a member of the EU and in the EU customs area – the economic case for keeping them was lost.
The UK could have chosen to retain freeports; nothing in EU law prevented them. Ending them was a political choice made by the then-administration.
Despite the absence of freeports, England remains home to 24 free zones, which operate on the same principle: in the Tees Valley and Manchester.
THE BENEFITS FOR PEMBROKESHIRE
The Milford Haven Waterway, a busy energy industry hub, is also a sensitive marine environment.
Supporting a scheme which could potentially undermine the Haven Waterway’s environmental status while pursuing a green energy future will be a difficult balancing act.
Milford Haven Port Authority argues that locating a Freeport in Milford Haven makes sense due to the Haven Waterway’s status as a nationally strategic energy asset and a key trade hub for the British energy supply.
A Freeport, it claims, will be an essential vehicle to help safeguard the existing professional energy jobs and skillsets to utilise for low-carbon ambition while regenerating the economy.
The Port Authority says the port’s existing energy infrastructure presents the opportunity for large-scale hydrogen production and injection with minimal additional infrastructure requirements. Alongside strong wind, wave and tidal resources, deep water access has already accelerated an emerging renewable sector such as floating wind in the Celtic Sea.
The Authority claims that a Freeport could support supply chains from equipment manufacturing to system integration and power connectivity, helping companies develop bankable projects and lower energy costs for UK consumers.
The proximity to major shipping routes and the existence of LNG terminals mean the Haven Freeport could also support a cleaner global maritime sector.
NOT PLAIN SAILING
Although freeports could, theoretically, redress imbalances in the UK’s economy by encouraging economic activity in areas where the economy is weakest, a careful balance must be kept.
The use of government subsidies for freeports – whether through direct grants or tax breaks – potentially falls foul of the WTO rules upon which Westminster seems determined to trade.
While freeports are successful in stimulating investment and jobs in a range of locations worldwide, they are neither a “silver bullet” for all locations nor the only way of boosting the UK’s main global gateways.
Freeports are notorious globally for being used to evade tax, launder money, and ease the transportation of stolen or illicit goods.
Moreover, as the experience at the Teesside Freeport development shows, they can lack any form of accountability and create fewer and less widespread economic opportunities than hoped.
The financial scrutiny of the Teesside Freeport is not much more than zero, and a box-ticking exercise carried out without any forensic examination of where the money goes and how contracts are awarded.
Milford Haven Port Authority operates a trust port. There are no shareholders or owners, and, importantly, its Board has independence of action without independent oversight.
A freeport’s financial structure is, if anything, even more financially opaque.
As public money is being invested in a freeport, proper public scrutiny – not merely loose “oversight” or lip service -must be the minimum standard.
Moreover, a freeport could be a money pit and public funding magnet. Too big an opportunity and too large a political totem to allow to fail, even when its economics don’t add up, freeports could end up being propped up by public money while delivering less than promised on the tin.
THE COMPETITION
In all the positive publicity about a possible Freeport in Milford Haven, the Haven is not alone in wanting one.
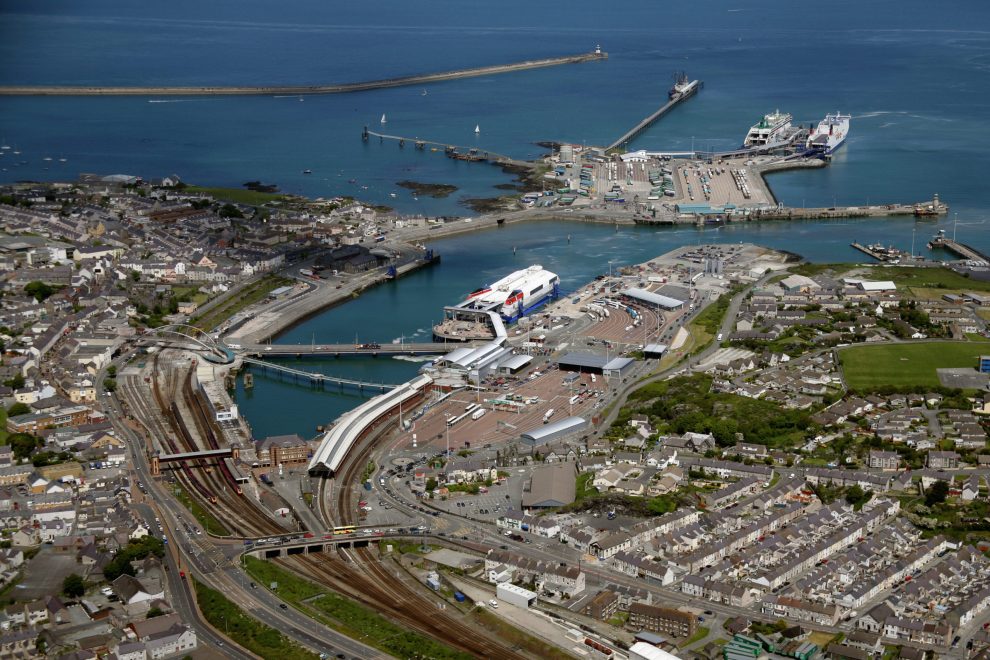
Holyhead is Wales’s largest Irish Sea port. It is also in the key marginal constituency of Anglesey.
The stalled Wylfa development for nuclear power (part of the UK’s Government economic and energy strategy) is also on the island, and an already massive and expanding wind farm lies off its coast.
Holyhead links the North Wales corridor to England’s northwest and the Midlands. Transport infrastructure is already better to and from Anglesey than from Pembrokeshire to those destinations and will need less investment.
Cardiff Airport is another potential rival and one that could be especially attractive to the Welsh Government.
Since it bought a controlling stake in the Airport, the Welsh Government has propped it up with loans and grants.
Without Welsh Government support, the Airport would be insolvent.
The Welsh Government might be persuaded that making Cardiff Airport the first of Wales’s freeports would kill two birds with one stone.
It would attract more air and freight traffic to the site and decrease the Airport’s reliance on financial help from the Welsh Government.
As with Holyhead, the transport and infrastructure links from Cardiff Airport to other parts of the UK – in this case, the Midlands, the M4 corridor, and Bristol – are superior to those connecting Milford Haven with those regions.
MOVING MONEY
A substantial concern expressed in a report on the Freeport scheme presented to the County Council is the undeniable fact they often do not create jobs but move them from one area to another.
The economic displacement of employment and funding opportunities could pull jobs and investments from one community to another.
If a new freeport only moved jobs and capital from (say) Newport to either Milford Haven or Holyhead, the economic case for their creation becomes – at best – shaky.
That raises the question of whether freeports provide value for public money through direct investment or tax relief.
Freeports could also be used to erode the high standards the UK currently places on workers’ rights and the environment.
Granting freeport operators carte-blanche to do what they want within a designated development area: for example, by allowing shortcuts through planning and environmental law or through allowing employment practices prevented elsewhere, involves trade-offs with unions and planning authorities could find problematic.
While jobs are needed, it is reasonable to ask what jobs and at what cost.
The experience of Welsh Enterprise Zones suggests few new jobs at a massive cost per head.
At a time of enormous hardship, it’s easy to be gulled by the prospect of large sums of public money and the prospect of that money pulling in private investment.
Tax and tariffs apart, a cautious individual might wonder why, if freeports are such a sure-fire thing, they need so much public money.