THE NATIONAL Rural Crime Network (NRCN) has welcomed a report released last Saturday (27 April) by the House of Lords Rural Economy Committee.
Julia Mulligan, Chair of the Network, gave oral evidence to the Committee at Westminster in November on rural crime and its impact.
She spoke about the National Rural Crime Survey’s results and the need for action to be taken to ensure the challenges it showed are addressed by the police, government and other organisations to keep rural communities safe and feeling safe.
The report outlines in stark terms the discrepancy in funding between urban and rural areas. It also calls for a comprehensive rural strategy, more measures to tackle rural criminality and the importance of ensuring a rural voice in Government.
The reported noted that, as in urban areas, crime can have a significant impact on rural businesses, economies and communities. However, the impact in rural areas can be greater, not least because of the isolation of some business properties (including farms), the larger areas and distances for police to cover and a lower police funding per head of population in rural areas than urban areas.
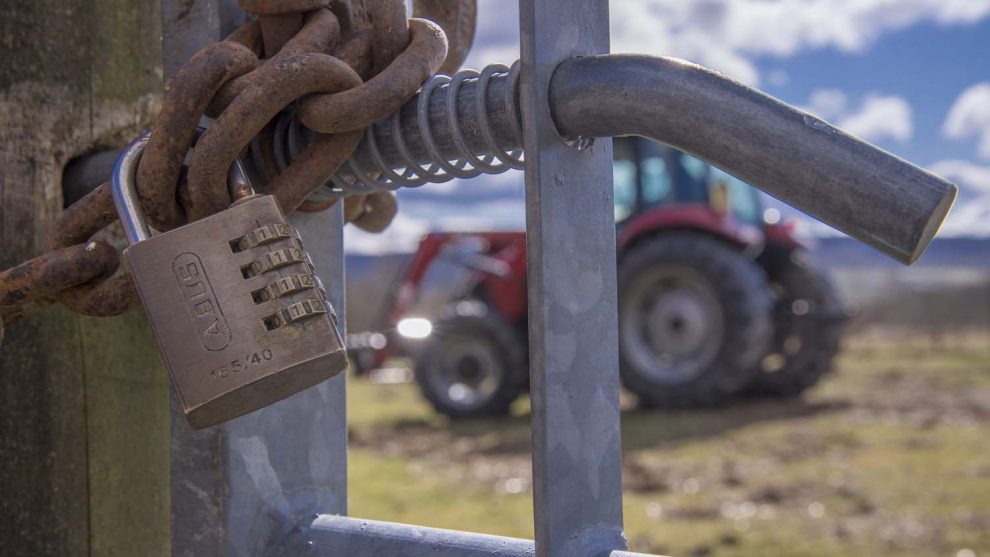
The Rural Crime Network Survey for 2018, which was commissioned by the National Rural Crime Network, a body made up of 30 Police and Crime Commissioners, found a poor perception of policing in rural communities. The survey found that only 27 per cent of 20,000 respondents believed their local police were doing a good job. 69 per cent of farmers and rural-specific business owners have been a victim of crime over the past 12 months and 60 per cent said they were fairly or very worried about being a victim of crime in future.
The monetary impact of rural crime has worsened in recent years, with the Rural Crime Network survey finding that the average cost of a crime to the victim had increased from £4,000 to £4,800 between 2015 and 2018.
Sarah Lee of the Countryside Alliance, who also sits on the board of the National Rural Crime Network, told the Committee that the financial impact of crime on rural businesses averages about £5,000, a potentially significant amount for a small rural business, and an increase of 13 per cent since 2015
Graham Biggs of the Rural Services Network told the Committee the main economic impact from rural crimes comes from the theft of agricultural implements and machinery.
The full cost of rural crimes is being underestimated. By way of example, Deputy Chief Constable Craig Naylor, the lead for rural crime for the National Police Chiefs’ Council explained that if a harvester is stolen, the cost of the stolen harvester will be recognised through the insurance claim while the cost of a crop not being harvested goes unreported.
Graham Biggs also told us that rural police forces are underfunded and receive less per person funding than urban counterparts.
According to the National Police Chiefs’ Council, on average, the 12 most rural police forces receive £100 per head of population compared to £158 for the 12 least rural forces, representing a difference of £58 (37 per cent) less funding for most rural police forces.
Concerns were also expressed over the closure of rural police stations and of some magistrates’ courts that serviced rural areas. Julia Mulligan said “The force I operate in has 11,000 police officers, which is down in the last five years from over 13,000. We are in a position where, with the current budget situation, we will have to cut again next year. We will be a good percentage point down from what our operating model was less than five years ago. Our demand has gone up”
As with other rural services, rural policing faces challenges of distances and sparsity. The Lord Bishop of St Albans commented on the absence of police in rural areas, noting that “if you call the police in a remote rural area there is probably no policeman for 20 or 40 miles”
Among the recommendations in the report:
• ‘The impact of rural crime on rural economies is a significant concern. More needs to be done by Government to better understand, track and respond to rural criminality.’ (recommendation 117)
• ‘We would also like to see new measures introduced [on fly-tipping] to ensure that farmers and land-owners do not have to pay for the cost of clean-up of rubbish that is dumped on their land.’ (recommendation 118)
• ‘Magistrates, Courts and the Crown Prosecution Service should be trained to better understand the scale and impact of rural crime. Reforms to sentencing guidelines should be considered, where appropriate, to widen the range of possible sentences to better reflect the seriousness of some crimes.’ (recommendation 119)
Julia Mulligan, Chair of the National Rural Crime Network and North Yorkshire Police, Fire and Crime Commissioner, said: “This is a welcome and comprehensive report on all aspects of the rural economy and its impact on those who live and work in the countryside.
“The House of Lords Committee is correct that we need to do more to tackle crime and the fear of crime in rural areas – and ensure the police and other organisations have the resources to do that.
“It reinforces the findings of our National Rural Crime Survey which found the impact of crime – from anti-social behaviour to fly-tipping and speeding – is significant and that action needs to be taken. It is vital the government listens.
“We will continue to fight for rural communities, who should not have to put up with sub-standard services just because of where they live. I hope this report makes a difference because things need to change, and fast.”