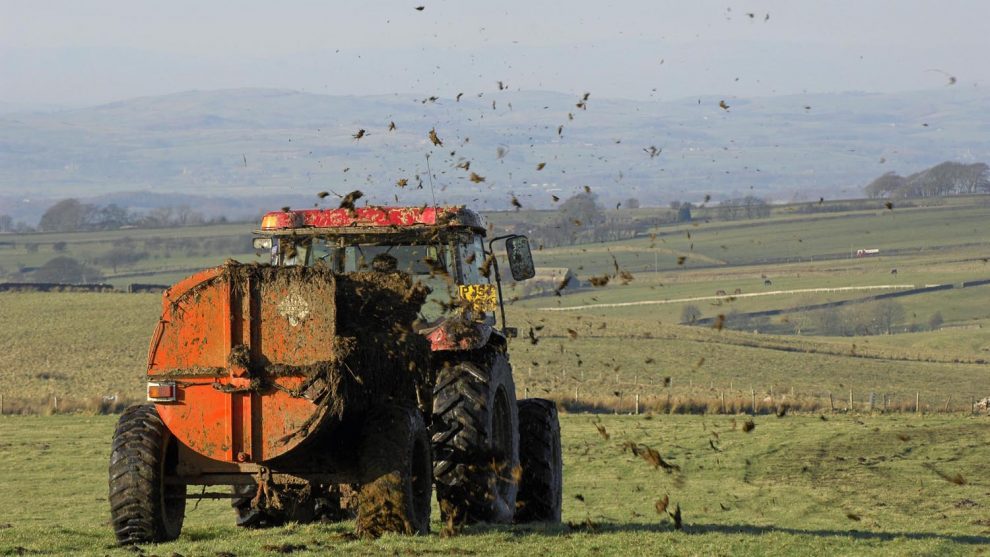
NFU CYMRU has urged Welsh Government to consider a ‘workable alternative’ to reducing nitrates from agriculture to prevent further extension of Nitrate Vulnerable Zones (NVZs) in Wales.
The Union has written to the Cabinet Secretary for Environment and Rural Affairs, Lesley Griffiths AM, to reiterate earlier commitments to provide the resources required to support the development of such a solution as an alternative to NVZ proposals that could see the percentage of NVZs in Wales rise from 2.4% to 8% – or even a leap to an all territory approach covering the whole of Wales.
The Cabinet Secretary is expected to make an announcement on the NVZ designations before the end of 2017.
The new option put forward by NFU Cymru has been designed by farmers and builds on an off-set scheme that has been operating successfully by a group of First Milk dairy farmers in the Cleddau Catchment in Pembrokeshire. The approach requires farmers to select mitigating measures appropriate to their system. The scheme is recorded, audited by Natural Resources Wales (NRW) and meets the strict requirements of the Environmental Permitting and Habitats Regulations – on average each participating farm is saving a tonne of nutrient annually.
This model has significant potential to be developed and could deliver measurable reductions in nitrates, well above those modelled for the NVZ Action Programme, as well as broader environmental benefits.
Speaking ahead of the Welsh Dairy Show in Carmarthen, NFU Cymru President Stephen James said: “We are clear that any new designations will have a significant impact upon the businesses of farmers and, severely hit the rural economy of these areas. The costs associated with implementation vastly outweigh the benefits to water quality. Farmers do, however, recognise their role in improving water quality and have developed a workable solution that has the potential to deliver far more than can be achieved through the NVZ Action Programme.
“The measures suggested with this approach address diffuse pollution issues and also provide habitat improvement. Developed in partnership, we believe they are likely to engender the confidence and ‘buy-in’ of the farming community – our own survey work shows significant willing from Welsh farmers to address the issue of nitrate pollution and improve water quality.
“This proposal is a workable alternative to the options currently on the table and delivers farmer-led solutions that bring environmental benefits – something that all parties share a vested interest in achieving; also aligning with Wales’ new legislative framework which presents opportunities and the flexibility to move forward and make progress on water quality issues on a different basis than previously.
“An alternative approach, rather than an unwieldly EU directive, will enable us to develop, grow and realise NFU Cymru’s vision of a productive, progressive and profitable industry that will deliver jobs, growth and investment for Wales and we have extended an offer to the Cabinet Secretary to join us on a visit to farms in West Wales to see the benefits of this approach for herself.”
WHAT IS AN NVZ?
An NVZ designation places a series of restrictions on farmers’ ability to use certain types of fertiliser on their land at prescribed times of the year. The aim is to reduce the effect that run off from agricultural land has on the environment.
The effects of nitrate pollution on the aquatic environment can be significant. High nitrate concentrations can cause a deterioration in water quality and disturb the ecosystems of rivers and other watercourses. Over enrichment of water can lead to a depletion of oxygen levels leading to a loss of marine life and causes increased toxic and non-toxic algal blooms, which make the situation worse by reducing water transparency. Nitrate pollution can reduce not only the diversity of plant life but also damage fish and shellfish stocks, as the algae consume the available oxygen suffocating other life.
In the worst case scenario, anaerobic (oxygen-starved) conditions cause toxic bacteria to thrive and can create ‘dead zones’.
In order to tackle the threat posed by nitrate pollution, in 1991 the European Union adopted rules governing nitrate pollution and sought to regulate the extent of nitrate pollution entering the environment.
WG APPROACH LACKS EVIDENCE
FUW Senior Policy Officer Dr Hazel Wright, who has been representing the Union in the review process, said: ‘‘The FUW has been involved in the NVZ review and has made successful representations on several designations, which resulted in their removal from the discrete areas option of the consultation.
“However, the number of proposed new designations remain a concern and the FUW continues to reiterate the operational and financial impacts those designations would have upon farms that reside within an NVZ area. Given such costs, there must be full justification for any proposed increases in designation.”
Two options outlined in the consultation include the continuation of the discrete approach to designation or the designation of the whole of Wales as a NVZ. A continuation of the discrete approach would see an increase in the amount of NVZ designations in Wales rise from 2.4% to 8%. This would mean significant changes to NVZ designation in counties such as Pembrokeshire, Carmarthen and Anglesey.
“The FUW remains resolutely against the option to apply the action programme throughout the whole of Wales as this would require all landowners to comply with the NVZ action programme measures.
“There is a distinct lack of evidence for a whole territory approach and the difficulties and costs associated with regulatory compliance for farms whose land does not drain into nitrate polluted waters, makes this option both unwarranted and unreasonably excessive,” added Dr Wright.

















Add Comment